Products and Information
3-Sigma MBS
Read
⊕ Rope used for rescue, rope access or work at height should be specifically designed and intended for life safety use.
⊕ Tested and marked in accordance with a relevant standard.
⊕ USA most respected life safety rope standards (NFPA 2500 and ANSI Z359 and ANSI Z459) refer back to Cordage Institute Life Safety Rope Test Methods (CI1801).
- Unique method of reporting Minimum Breaking Strength.
- break testing at least five samples of rope
- calculating three standard deviations below the mean of those results.

⊕ EXAMPLE: 5 samples from five different lots of rope
- Lab wll pull test the rope to failure.
- Inevitably slightly different results with each test.
- what is the RIGHT number to report?
⊕ Actual numbers Scenario
- (6500) pounds
- (6750) pounds
- (6675) pounds
- (7005) pounds
- (6925) pounds
⊕ What number do we report?
- best result? 7005 pounds force.
- worst-case? 6500 pounds (about 500 pounds less than the best result)
- What aboutnatural variation in materials testing – are these reliable?

⊕ Cordage Institute test method (and the NFPA and ANSI standards that refer back to it)
- mathematical approach to ensure statistical significance
- Other Standdards(Euro-norms or CE) do not use this method
⊕ “3-sigma MBS” method.
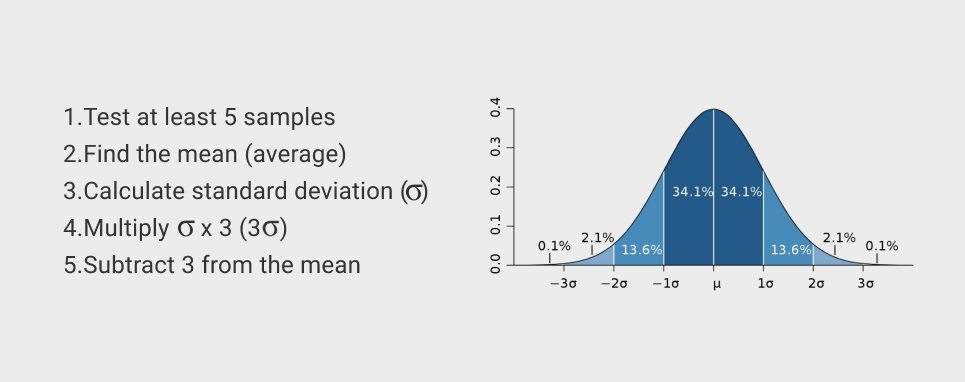
⊕ At least five tests from different manufacturing lots, very specific test method
- calculate the MEAN AVERAGE
- SUBRACT three standard deviations from the mean
- 7% confidence
⊕ Practical view, sample set.
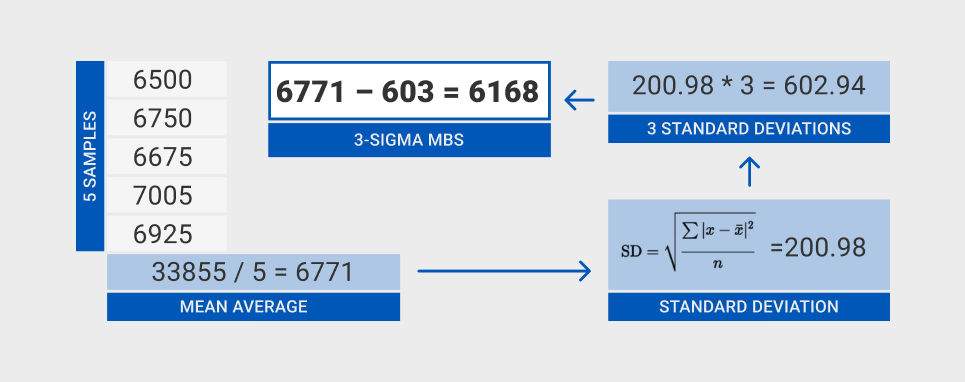
- add up the sum of all our test results (33,855)
- THEN we divide by the number of tests (5)
- Average – 6771
- which is six thousand seven hundred seventy one
- Calculate standard deviation from mean average (200lbf)
- symbol called SIGMA.
- multiply Standard Deviation by THREE…. 3x 200.98 = 602.94
- refer to this as THREE SIGMA
- SUBTRACT that 3-Sigma number from the MEAN AVERAGE
- 6771 – 602.94 = 6168
- 900 pounds less than the best test
- 332 pounds lower than even the worst test
⊕ THIS WILL affect your safety factor calculations!
- 3s mbs is a number that you can rely on
- 7% confidence
⊕ NOT all standards use this method
- even within Cordage Institute, only the Life Safety Rope standard uses it
- many standards don’t even specify how the reported MBS is supposed to be derived
- only that the strength of tested samples needs to be greater than X





Dwayne Witter
Great information and delivery. You broke it down so well. Thanks Loui!